How to calculate the current ratio in Excel
This allows a company to better gauge funding capabilities by omitting implications created by accounting entries. The current ratio can be a useful measure of a company’s short-term solvency when it is placed in the context of what has been historically normal for the company and its peer group. It also 15 tax deductions and benefits for the self offers more insight when calculated repeatedly over several periods. A current ratio that is in line with the industry average or slightly higher is generally considered acceptable. A current ratio that is lower than the industry average may indicate a higher risk of distress or default by the company.
Company
- Current assets like cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities can easily be converted into cash in the short term.
- Sometimes this is the result of poor collections of accounts receivable.
- Sage makes no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness or accuracy of this article and related content.
- In this case, it may not be fully using its workable assets to continue to grow.
My Trading Challenge students get access to webinars, video lessons, my DVDs, my incredible chat room, and more. Every industry has different ratio averages based on factors that can tell you about a company’s overall health. Therefore, you CAN calculate and perform interpretations every quarter. If it needs cash badly, a sketchy company may pump its stock up, then rip your heart out with a toxic offering. When you’re in an overnight position after the market closes, you’re stuck.
Balance Sheet Assumptions
Generally, the assumption is made that the higher the current ratio, the better the creditors’ position due to the higher probability that debts will be paid when due. Industries with predictable, recurring revenue, such as consumer goods, often have lower current ratios while cyclical industries, such as construction, have high current ratios. Even within an industry, current ratios can differ between companies. Another practical measure of a company’s liquidity is the quick ratio, otherwise known as the “acid-test” ratio.
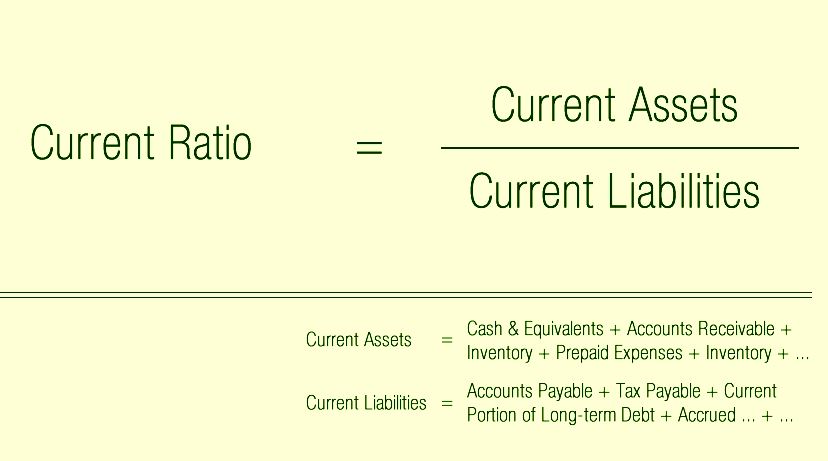
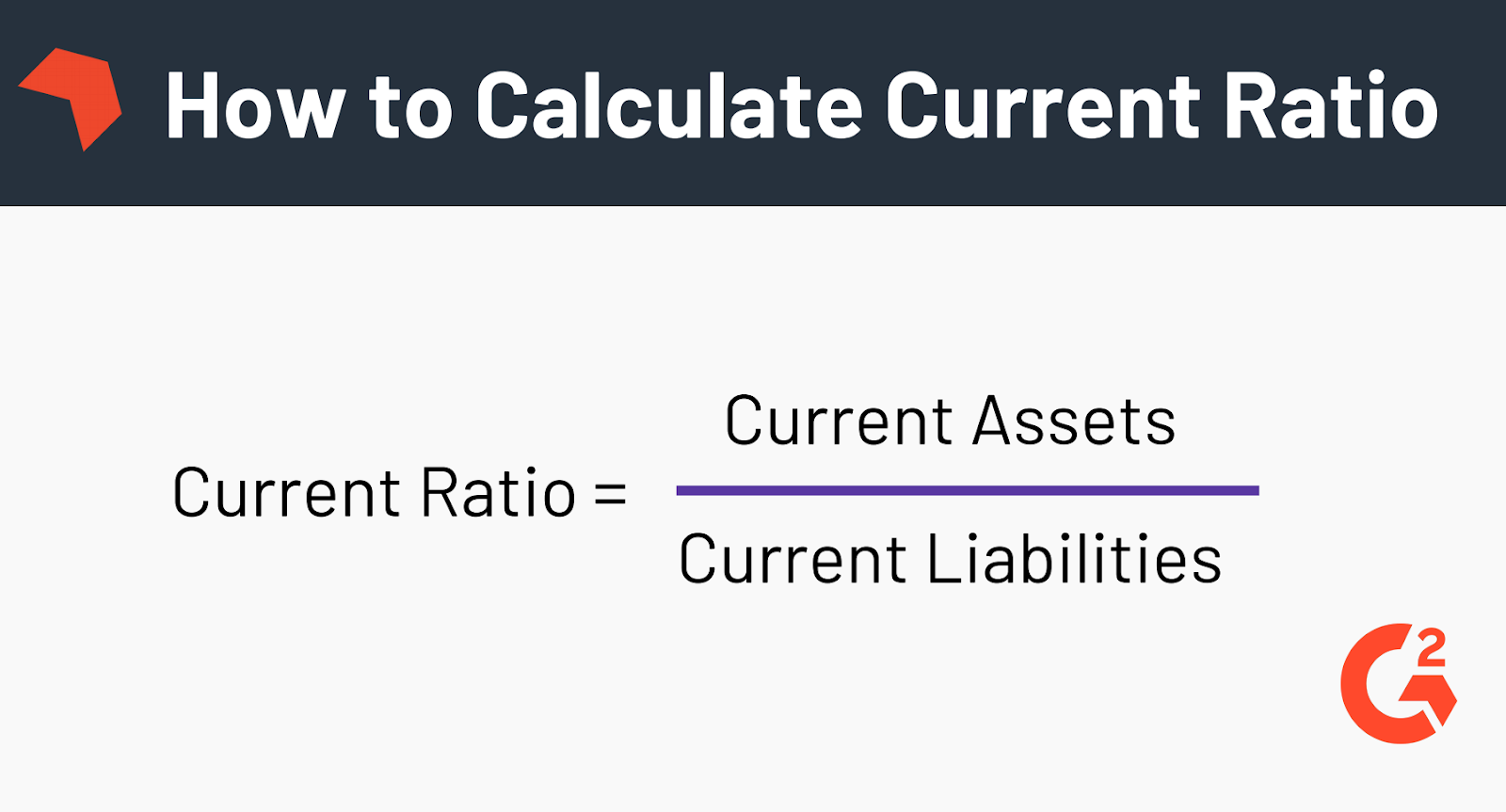
What is the formula for the Current Ratio?
However, you have to know that a high value of the current ratio is not always good for investors. A disproportionately high current ratio may point out that the company uses its current assets inefficiently or doesn’t use the opportunities to gain capital from external short-term financing sources. If so, we could expect a considerable drawdown in future earnings reports (check the maximum drawdown calculator for more details).
You can find them on your company’s balance sheet, alongside all of your other liabilities. The prevailing view of what constitutes a “good” ratio has been changing in recent years, as more companies have looked to the future rather than just the current moment. Some lenders and investors have been looking for a 2-3 ratio, while others have said 1 to 1 is good enough. It all depends on what you’re trying to achieve as a business owner or investor. In actual practice, the current ratio tends to vary by the type and nature of the business.
Formula
With that said, the required inputs can be calculated using the following formulas. We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Join our Sage City community to speak with business people like you. Get a roundup of our best business advice in your inbox every month. Liquidity is crucial for financial institutions to meet sudden cash demands during market volatility.
Public companies don’t report their current ratio, though all the information needed to calculate the ratio is contained in the company’s financial statements. The quick ratio is a strategic tool that offers insight into your company’s liquidity and financial readiness. Through this proactive measure, you effectively improve your firm’s quick ratio from 1.2 to 1.4, strengthening your short-term liquidity position and mitigating potential financial strain. The cash ratio is ideal for assessing immediate liquidity without assuming future collections, but it may be too conservative for businesses that collect payments reliably, like SaaS or professional services.
Perhaps this inventory is overstocked or unwanted, which eventually may reduce its value on the balance sheet. Company B has more cash, which is the most liquid asset, and more accounts receivable, which could be collected more quickly than liquidating inventory. Although the total value of current assets matches, Company B is in a more liquid, solvent position. Current assets listed on a company’s balance sheet include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and other current assets (OCA) that are expected to be liquidated or turned into cash in less than one year. This is why it is helpful to compare a company’s current ratio to those of similarly-sized businesses within the same industry.
Current assets include only those assets that take the form of cash or cash equivalents, such as stocks or other marketable securities that can be liquidated quickly. Current liabilities consist of only those debts that become due within the next year. By dividing the current assets by the current liabilities, the current ratio reflects the degree to which a company’s short-term resources outstrip its debts. The current ratio equation is a crucial financial metric, that assesses a company’s short-term liquidity by comparing its current assets to its current liabilities.
The study authors found that 97% of traders with more than 300 days actively trading lost money, and only 1.1% earned more than the Brazilian minimum wage ($16 USD per day). Its simple to calculate, which makes it attractive to traders and investors. Seasonality is normally seen in seasonal commodity-related businesses where raw materials like sugar, wheat, etc., are required. Such purchases are done annually, depending on availability, and are consumed throughout the year.
